The trigone bone is also known as the extra bone and also as the Os Trigonum Syndrome. It is an extra bone of small size that is located in the ankle, and that a priori we should not worry about it, unless the pain is intense, that is where surgery comes into play.
It seems a joke, but it is not. There are those who have an extra bone in their body, specifically in the ankle, apart from the 206 bones that we have in adulthood. Yes, it is that, at birth, we come into this world with 300 bones, and a hundred of them fuse to give rise to the 206 that we have in the last days of our lives.
This extra bone is known as the trigone bone, and we will be very surprised how it is formed, how it is discovered, and what symptoms it causes. In addition, it is related to what we have explained before, that we are born with 300 bones and in adulthood we have 100 less.
Throughout this text, we will explain everything about this tiny bone, where it is located from, what causes it, whether it hurts or not, and how it is eliminated forever. We will also know which athletes are more likely to carry this distressing situation.
What is it?
The Os Trigonum Syndrome is a very small bone that is installed on the posterolateral aspect of the talus formed from an isolated or separated ossification center that for certain reasons cannot join the talus.
Ok, it is likely that we have not understood anything, so we are going to explain it in other words. It's about a small bone that arises singly at the back of the ankle and arises between the heel and the talus which is the ankle bone.
It arises from a kind of error, and the symptoms are very clear. In addition, it is estimated that up to 15% of the world population has it or is going to have it and does not know it. Sometimes it causes pain, and other times it is discovered randomly after an X-ray of the foot.

Why does it occur?
As we have said before, this is a kind of error. It can occur on one foot or both and it is about something congenitalThat is, it is present from birth. When it becomes most evident is in adolescence and it arises because the ankle bone does not fuse properly and that small bone that we now call the trigone bone appears.
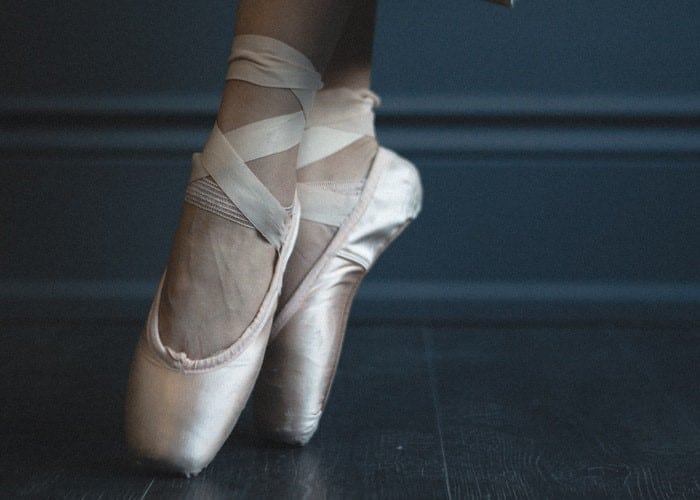
For it to make an appearance, sometimes a previous injury such as a sprain is necessary. The syndrome is a very common injury in those people who frequently walk on tiptoes or bring their toes to the ground, forcing hyperflexion of the sole of the foot.
this bone causes pain and creates instability, which can trigger another series of injuries throughout the foot and legs. It is a common pathology in soccer players, ballet dancers and other similar sports.
Symptom
The symptoms are clear, and with a simple X-ray the cause of the pain can be located. We are going to list the most common symptoms, which may or may not coincide with our case. Remember that it is a congenital problem and if we do not practice one of those sports that we have discussed before, it is quite likely that we will not develop the syndrome.
- sharp and deep pain on the back of the ankle, especially when we press with the big toe.
- Much sensitivity in the area with touch.
- Inflammation and swelling in the area.
- Difficulty maintaining balance.
- Pain when turning the ankle.

Transmission
The treatment of this injury goes through different phases, depending on the pain, the sport that is performed, the exact area of the bone, whether or not it prevents the patient from leading a normal life, etc. As a general rule, there are different options, but there is always the operation as a last resort, and we will talk about it later.
- Maximum rest and do not support the injured foot until the pain subsides.
- Anti-inflammatories (preferably non-steroidal), as long as it is not contradictory because the patient is already taking other medication for another disease or ailment.
- Ice to relieve swelling and pain. The ice pack or frozen bag should be placed on the affected area, but not directly or it will damage our skin, rather there is a cloth or cloth between our skin and the ice.
- Temporary immobilization is usually one of the most chosen options, along with medications. An orthopedic boot is placed that limits the movements of the ankle.
- An injection of cortisone, although many specialists advise against it, since it has a very short useful life and finally you have to go through the operating room.
Almost always a combination of several of these treatments is prescribed, but if the pain is very great, surgery is usually done directly. Of course, as a general rule, the symptoms usually disappear with these non-surgical remedies.
When to have surgery
Do not panic, it is an extra bone that is useless and its extraction is carried out by means of a simple surgery with a short recovery period. The operation is recommended at times when the pain no longer subsides with any of the non-surgical options and even prevents the development of a normal life such as walking, maintaining balance, working, sleeping, training, etc.
Surgery will alleviate this pain by removing that small bone, no extra intervention will be necessary, nor is collateral damage done to tendons, ligaments, muscles, bones and joints. It is recommended to go to a doctor specialized in foot traumatology, so that he can explain step by step what the intervention consists of, what the postoperative period will be like, when we can return to training, etc.
We can request the operation, but doctors will always recommend non-surgical options first, unless our professional career is at stake, or similar situations where the pain is so intense that we are losing mobility, we are afraid to walk or we cannot rest. In short, that subtracts our quality of life.